Learning & education

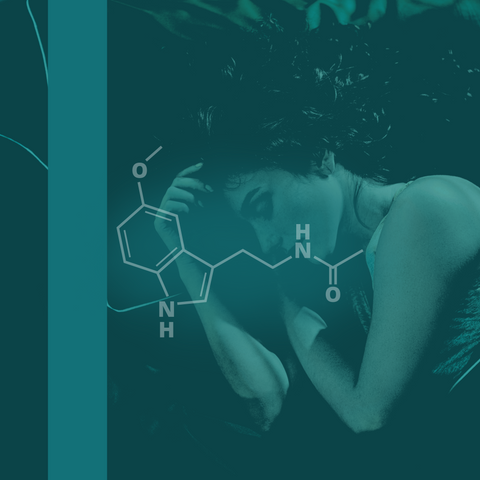
In this article, we will look at what’s known about combining melatonin with common psychedelics, based on the current evidence available. We discuss how melatonin might enhance, dampen, or otherwise alter psychedelic effects, how it could influence sleep and neuroplasticity, and what gaps remain in the research base.

This article seeks to examine the multifaceted ways in which melatonin may support endurance athletes and recreational exercisers alike, delving into mechanistic insights, safety profile, and practical considerations for supplementation.
In this article, we'll be exploring 4 ways to naturally increase your melatonin levels through some dietary and lifestyle changes, whether it be lessening exposure to room light, eating foods like eggs and fish more often, or having one less cup of coffee!

Melatonin is involved in sleep regulation and the circadian rhythm [2]. However, melatonin also plays other roles in the human body as in the immune system [3], in cancers [4], and even in energy metabolism [5]. Previously, we've discussed melatonin supplementation, melatonin's anticancer potential, and its effects on depression and anxiety. In this article, we'll focus on melatonin's role in diabetes and weight loss.

Have you ever felt exhaustion dragging at your eyelids, only to find yourself wide awake staring at the ceiling as you lie in bed, not feeling sleepy at all despite being tired all day?
It's a frustrating paradox — you're feeling tired but can't sleep. This experience, known as paradoxical insomnia, affects millions of people worldwide alongside those with sleep disorders.

